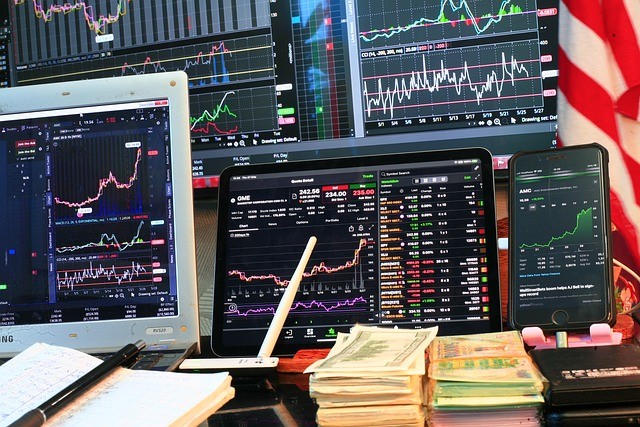
Investing in the stock market can seem daunting at first, but with the right knowledge and strategy, it can be a powerful way to build wealth over time. Whether you’re looking to supplement your income, save for retirement, or simply explore the world of finance, understanding the basics of stock market investing is essential. This guide will walk you through the fundamentals of stock market investing, helping you get started on your investment journey.
Understanding the Stock Market
The stock market is a marketplace where investors buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. These shares represent ownership in the companies, and their value can fluctuate based on a variety of factors, including the company’s performance, economic conditions, and market sentiment.
The two main components of the stock market are:
- Stock Exchanges: Platforms where stocks are listed and traded. Major exchanges include the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Markets: Where stocks not listed on major exchanges are traded. This includes smaller and less regulated companies.
Setting Your Investment Goals
Before you start investing, it’s crucial to define your financial goals. Are you investing for short-term gains, long-term growth, or retirement? Your goals will determine your investment strategy and risk tolerance.
- Short-Term Goals: Investing with a horizon of less than five years. This might include saving for a down payment on a house or a vacation.
- Long-Term Goals: Investing with a horizon of more than five years, such as retirement or education funds.
Building a Diversified Portfolio
Diversification is key to managing risk in your investment portfolio. Instead of putting all your money into one stock or sector, spread it across different types of investments. A diversified portfolio may include:
- Stocks: Shares in individual companies.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations.
- Mutual Funds: Investment funds that pool money from many investors to buy a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Similar to mutual funds but traded like stocks on an exchange.
Choosing the Right Investment Strategy
There are several strategies for investing in the stock market, each with its own advantages and risks:
- Buy and Hold: Investing in stocks with the intention of holding them for a long period, regardless of short-term market fluctuations.
- Active Trading: Buying and selling stocks frequently to take advantage of short-term price movements. This requires significant time and research.
- Index Investing: Investing in index funds or ETFs that track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. This strategy aims to match the market’s performance rather than outperform it.
Researching and Selecting Stocks
Before investing in a stock, it’s important to conduct thorough research. Consider the following factors:
- Company Fundamentals: Analyze financial statements, earnings reports, and business models.
- Industry Trends: Understand the industry in which the company operates and its growth potential.
- Valuation Metrics: Use metrics such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio and price-to-book (P/B) ratio to assess if a stock is fairly valued.
Managing Risk
All investments carry risk, but there are ways to manage and mitigate it:
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically sell a stock if its price falls below a certain level to limit potential losses.
- Invest in Quality Stocks: Focus on companies with strong fundamentals and a track record of performance.
- Review Your Portfolio Regularly: Rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation and adjust for changing market conditions.
Staying Informed and Educated
The stock market is dynamic, and staying informed is crucial for successful investing. Follow financial news, read market analysis, and consider taking courses or consulting with financial advisors to deepen your understanding.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Lack of Research: Avoid investing in stocks without proper research and understanding.
- Emotional Investing: Don’t let emotions drive your investment decisions. Stick to your strategy and goals.
- Overtrading: Frequent trading can lead to higher transaction costs and taxes, which may erode your returns.
Conclusion
Investing in the stock market offers significant opportunities for wealth accumulation, but it requires careful planning, research, and risk management. By setting clear goals, diversifying your portfolio, and staying informed, you can navigate the complexities of the stock market and work towards achieving your financial objectives. Remember, investing is a long-term endeavor, and patience and discipline are key to success.